Salamander floating wind project to collaborate with Scottish universities on marine environment study
Salamander, a joint venture between Ørsted, Simply Blue Group and Subsea7, has partnered with two Scottish universities to investigate any potential impact of floating windfarms on marine ecosystems.
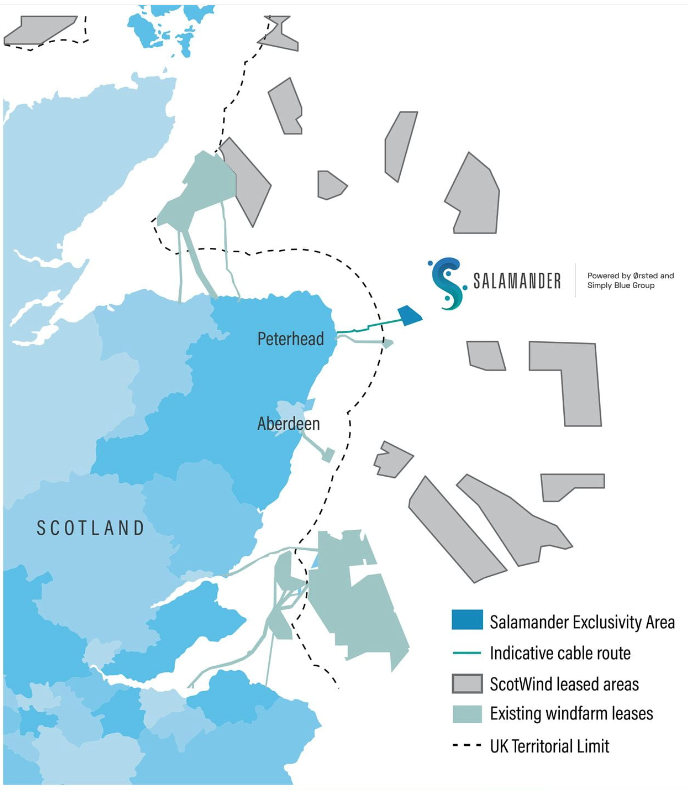
The PREDICT 2.0 initiative forms part of a research programme led by experts at the University of the Highlands and Islands’ (UHI) Environmental Research Institute and the University of Aberdeen, and is designed to develop a better understanding of fish migration patterns.
With significant renewable infrastructure set to be installed in coming years, any potential impacts of future developments on fish and their predators must be considered. The proposed Salamander site will be used as a monitoring base to gather data on the drivers of variation in fish movement and availability as prey.
Hugh Yendole, Project Director at Salamander said: “We are proud to be collaborating with two leading universities on this crucial piece of research. As a stepping stone project, part of our role is to prepare the industry to deliver for the renewable needs of the future, and this study will provide real insight into how we can do so in the most sustainable way possible.
“Projections place offshore wind at the centre of the Scottish energy mix in the coming years, and we are keen to ensure this is done in a way that protects our planet as well as our people.”
Dr Benjamin Williamson, Associate Professor of Energy at UHI said: “Marine sensing is vital to understand the environment around floating offshore wind farms. Robust information and evidence are needed to inform where offshore wind developments should be located to better protect marine ecosystems.”
Experts will deploy various sensors that can be used to identify fish presence and behaviour in the site, whilst assessing how these change over time.
The original PREDICT programme enhanced understanding of fish migration patterns and provided a vision for next generation monitoring techniques. The second phase is expected to further such research, working with the Salamander team to investigate the likely impacts of floating offshore wind farms on marine life.
To be located 35 km off the coast of Peterhead, the 100 MW Salamander floating offshore wind farm will generate enough green energy to power 100,000 Scottish homes. If consented, the project will provide key insights and opportunities for the Scottish supply chain for future larger-scale developments in Scottish waters and further afield, ahead of the larger-scale ScotWind build out.
